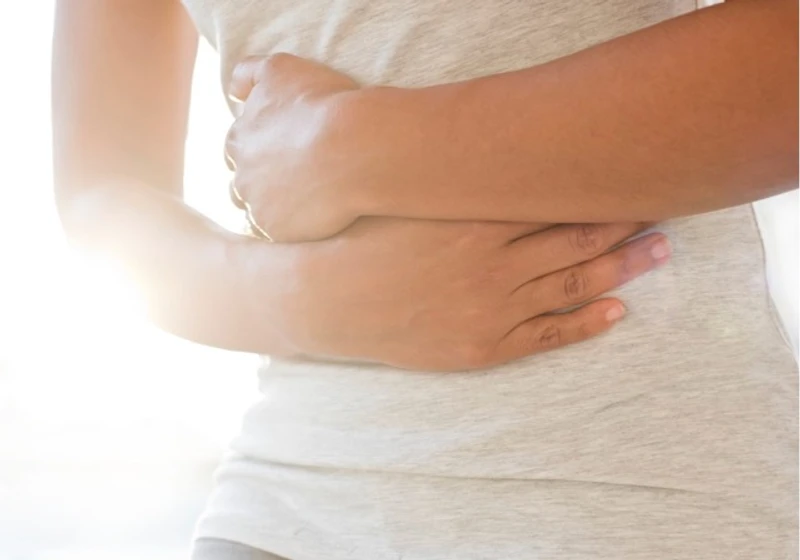
What is IBS?

Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be a source of significant discomfort and disruption to daily life. While IBS is a chronic condition, its symptoms can often be managed effectively, and one key avenue for relief is through dietary modifications. In this article, we will explore what IBS is, its prevalence, common symptoms, and how changing your diet can offer a solution for a better quality of life.

What is IBS?
IBS is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a group of symptoms related to the digestive system. Unlike some other digestive conditions, IBS does not cause structural damage to the digestive tract but rather disrupts the normal functioning of the digestive system. It is considered a "functional" disorder because its primary impact is on how the gut works, rather than on its physical structure.
Prevalence of IBS
IBS is one of the most common gastrointestinal disorders globally. It affects people of all ages, though it is most commonly diagnosed in individuals under the age of 50. The prevalence of IBS varies by region and population, but on average, it affects around 10-15% of the population. It is estimated that twice as many women as men are diagnosed with IBS, although this may be due in part to differences in healthcare-seeking behavior.
Common Symptoms of IBS
The symptoms of IBS can vary from person to person, but some of the most common include:
- Abdominal Pain and Cramping: Pain is often described as sharp or cramp-like and can occur anywhere in the abdomen.
- Changes in Bowel Habits: This can include diarrhea, constipation, or alternating between the two.
- Bloating: A feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdomen, often accompanied by visible distention.
- Gas and Flatulence: Increased gas production and the sensation of needing to pass gas frequently.
- Urgency: A sudden and strong urge to have a bowel movement.
- Mucus in Stool: Some people with IBS may notice mucus in their stool.
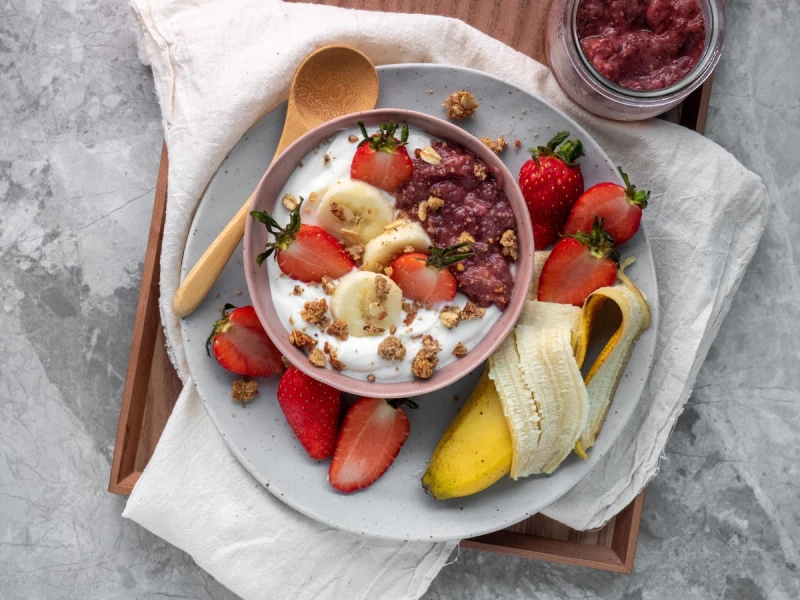
Dietary Modifications as a Solution
While there is no cure for IBS, many people find significant relief from their symptoms through dietary modifications. The relationship between diet and IBS is complex and varies from person to person. Here are some dietary approaches that can help manage IBS:
- Low-FODMAP Diet: FODMAPs are certain types of carbohydrates that can ferment in the gut, leading to gas, bloating, and diarrhea in some people with IBS. A low-FODMAP diet involves avoiding high-FODMAP foods like certain fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and grains. The Noba app is a great tool for guiding you through the low FODMAP diet.
- Fiber Intake: Soluble fiber can help regulate bowel movements and reduce symptoms of IBS. Foods like oats and psyllium husk are good sources of soluble fiber.
- Probiotics: Probiotic supplements or foods containing live beneficial bacteria can help regulate gut flora and improve symptoms for some individuals with IBS.
- Food Diary: Keeping a food diary can help identify trigger foods that worsen IBS symptoms, allowing individuals to avoid them. In the Noba app you can register what you eat, what symptoms you have and much more, enabling you to get a full overview of your IBS.
- Hydration: Drinking enough water is essential to prevent constipation, a common symptom of IBS.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate IBS symptoms. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can be helpful.
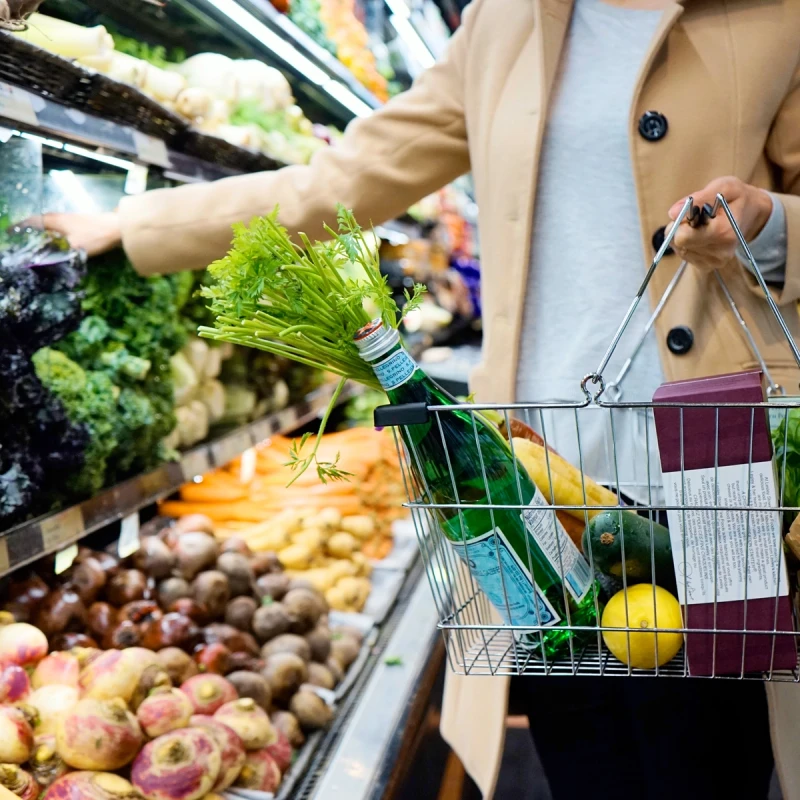

IBS is a prevalent and often debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it cannot be cured, it can be effectively managed. One of the most accessible and impactful ways to manage IBS symptoms is through dietary modifications.
Noba is made in collaboration with experts on the low FODMAP diet and gut health, and is daily helping tens of thousands of people with managing their IBS symptoms. You will get an overview over the food in your local supermarkets, and see whether or not they might cause symptoms.
Get started today by downloading our app on either App Store or Google Play.